Metal Free Zirconia Crown v/s Porcelain Fused to Metal Crown
A general visit to the dentist for getting a crown/Bridge may sometimes leave you puzzled when you are given certain options to choose from. And you might be unsure about which one to choose. This article will help you know in detail about:
- Different materials used to fabricate dental crowns
- What are Porcelain fused to metal crowns?
- Are there any limitations in Porcelain fused to metal crowns?
- What is a zirconia (all ceramic) crown?
- Is Zirconia better than Porcelain fused to metal crown? How?
- How does tooth reduction influence the prognosis of a crown?
- Types of Zirconia crowns
- Which Dental crown will be the ideal choice?
Different materials used to fabricate dental crowns
Dental crowns or caps are one of the frequently advised treatments in most of the patients. They are indicated in many conditions like a broken tooth, root canal treated tooth, replacement of a missing tooth etc. Metal was the very first material used in fabricating dental crowns as they were supposed to be having good strength. Over the years, various other materials were used in the manufacture of dental crowns like gold, resin, porcelain, porcelain fused to metal, or Zirconia, most of which are obsolete now. Among these, PFM crowns are still currently, the most widely used. But Zirconia is gaining popularity in terms of function and aesthetics.
| Type of crown | Composition | Strength | Aesthetics | Longevity | Amount of tooth to be removed | Biocompatibility |
| Metal | Gold Stainless steel | High | Unesthetic | Great | Less | Metal allergies can be seen |
| Porcelain fused to Base metal | Ceramic + Chromium/Nickle/beryllium/cobalt | High | Unesthetic | Ceramic layer chips off | More (0.5mm for metal +1.5mm for ceramic) | Metal allergies can be seen |
| Porcelain fused to noble metal | Ceramic + Gold/platinum/palladium | High | Unesthetic | Ceramic layer chips off | More (0.5mm for metal +1.5mm for ceramic) | Metal allergies can be seen |
| Resin | Polymethylmethacrylate | Very less | Good | Poor | More | Allergic reactions are rare |
| Emax | Lithium disilicate | High | Aesthetic | Good | More | Biocompatible |
| Zirconia layered | Zirconium dioxide +Yittrium oxide +Ceramic | High | Highly Aesthetic | Great | Less (as less as 1mm is enough) | Biocompatible |
| Zirconia monolith | Zirconium dioxide +Yittrium oxide | Very high | Aesthetic | Great | Less (as less as 0.5mm is enough) | Biocompatible |
Porcelain fused to metal (PFM) crowns:
Porcelain Fused to Metal (PFM) crowns are the most extensively used ones in many dental practices. It has served a good purpose of restoring teeth and providing support to the teeth. Yet, they also have certain disadvantages, which compromises the quality of treatment to some extent. A newer material (Zirconia) has proved to be the best alternative of Porcelain fused to metal crowns. Few dentists are now exclusively using Metal free Zirconia crowns in their practice, in replacing missing teeth, be it a single dental crown or a long span dental bridge.
Does Porcelain fused to metal (PFM) crowns have any Disadvantages?
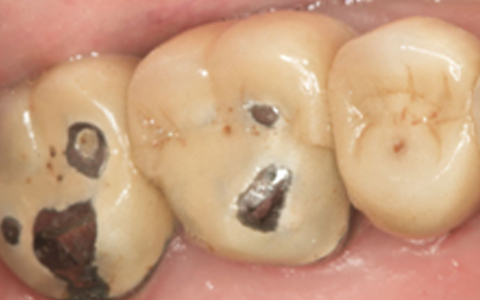
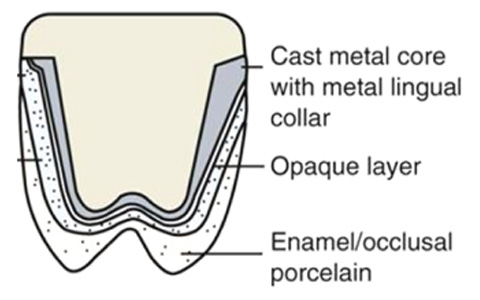
Yes!, Although Porcelain fused to metal crowns are widely used as dental crowns, it has certain limitations. Porcelain is a material with great esthetics; however, because of its brittle nature, it is prone to chipping when layered over metal. Metals like gold, or a mixture of others (cobalt, copper, beryllium etc.,) were also previously used because of their function and longevity, but were discontinued due to their appearance. A Porcelain fused to metal dental crown is the one, which has a metal crown upon which porcelain is layered to give natural tooth like appearance.
The brittle porcelain layer may fracture and chip off on chewing hard food, exposing the metal.
More tooth structure is needed to be removed to accommodate the thickness of crown (metal and porcelain).
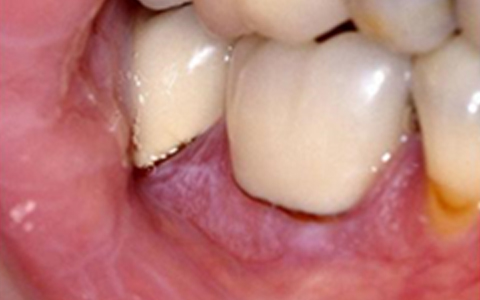
The metal part discolors the gum leaving a black colored line along the margins (called as Gum Tattoo).
Few patients may be allergic to the metal and develop allergic reactions.
IMMEDIATE-LOADING IMPLANTS
COMPLETED
REHABILITATIONS
IMPLANT CASES
What is a Metal free zirconia crown and how is it better than Porcelain fused to metal crown?
The drawbacks of Porcelain fused to metal crowns can be surpassed by Zirconia (Metal Free crowns) , which is derived from a material Zirconium. It simulates ceramic materials, has a remarkable strength and provides good natural tooth like appearance. It gives a good base for ceramic layering and can be stained to give a natural tooth like appearance. To summarize the advantages of metal free zirconia crown over Porcelain fused to metal crown;
1. Strength
Zirconia has a remarkably great strength.
These metal free zirconia crowns will not break as easily as porcelain and therefore overcomes chipping and fracture of the crown.
2. Thickness of the crowns
the metal free zirconia crowns are inherently strong even at a thickness of as low as 0.5mm. Porcelain fused to metal crowns on the other hand require around 1.5-2mm of thickness for the metal and porcelain layering over it, making it bulky.
3. Tooth reduction
Considering the required minimum thickness of the crowns, a greater amount of tooth structure should be reduced for Porcelain fused to metal crowns (minimum 2mm) whereas minimal tooth reduction is enough for metal free zirconia crowns (0.5mm). That is; porcelain fused metal crown preparation is relatively more when compared to that of porcelain fused to zirconia
4. Fracture of the crowns
Zirconia (Metal free crowns) has great strength and does not fracture or chip easily. Porcelain fused to metal crowns have porcelain layered on the metal which is brittle and can easily chip off exposing the metal.
5. Esthetics
Zirconia metal free crown is very much similar to ceramic materials. It can be stained and provides excellent natural tooth like appearance. On the contrary, although porcelain has good esthetic properties, the metal base alters its appearance and therefore compromises the esthetics.
6. Biocompatibility
Around 30% of the population is allergic to few metals. Porcelain fused to metal crowns in few patients show allergic reactions in their oral cavity. Metal Free Crowns on the other hand are very biocompatible and does not trigger any allergic reactions in the oral cavity.
7. Corrosion
The metal in Porcelain fused to metal crown undergoes corrosion over time while zirconia (Metal free crown) does not.
Advantages of Metal free Zirconia crowns over Porcelain Fused to Metal crowns
| ZIRCONIA CROWN | PORCELAIN FUSED TO METAL (PFM) CROWN |
| Exceptionally high strength | Less strength |
| Less tooth reduction | More tooth reduction |
| Does not fracture | Fractures and chips off easily |
| Highly esthetic | Not so esthetic |
| Not allergic | Can be allergic |
| Minimum thickness of 0.5mm is sufficient | Needs a minimum thickness of 1.5-2mm |
| Can be given in any patient | Not recommended in patients with bruxism |
| No gum discoloration | Gum Tattoo |
| Corrosion free | Metals corrode over time |
Types of Metal free Zirconia crowns
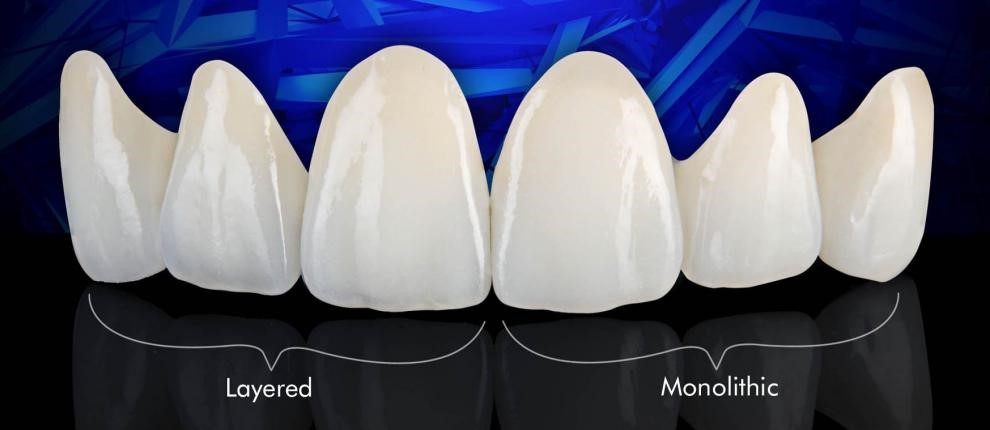
Monolithic and Layered Zirconia

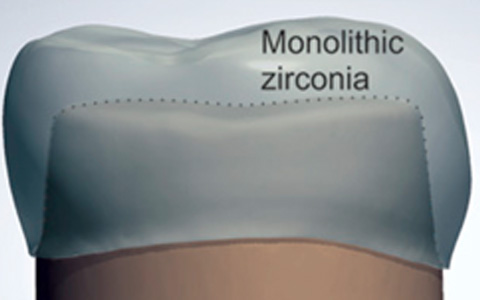
A monolithic (full contour) anatomical crown is made in a single block and has good strength. It is devoid of chipping and does not affect the opposing natural teeth, which makes it suitable for any patient. These monolithic crowns are therefore best used in replacing posterior teeth, which are primarily subjected to chewing forces.
The anterior teeth however need better translucency to best mimic the natural teeth. Metal free crowns in esthetic zones are hence layered with ceramic materials, for better staining and shading to get maximum simulation of natural teeth.
Why posterior crowns should not be layered?
(Importance of monolithic crowns for posterior teeth)

This will compromise the chewing capacity, reduce the height of the crown, may cause TMJ pain when multiple teeth are involved resulting in patient discomfort and dissatisfaction. Monolithic Zirconia metal free crowns are devoid of any layering and inherently possess all the cups and grooves, which will not chip off. It not only maintains the height of the back teeth, but also provides better chewing efficacy. Monolithic Zirconia, with all these advantages, proves to be the ideal choice for replacing posterior teeth.

Various brands of metal free crowns (zirconia) with different compositions are trying to enhance the translucency and colour of the crowns and bridges making it an ideal choice for replacing missing teeth.
So which crown will be the ideal choice?
The choice of the crown depends on the tooth that is being replaced. If it is the posterior teeth, where majority of the chewing forces are there, one can consider getting a PFM or a monolithic metal free zirconia crown. But as the chewing forces are greater, the porcelain may cause an unintended damage to the opposing natural tooth. Apart from which, the porcelain may eventually be chipped off leaving a flat surface with the metal part exposed. Hence a monolithic zirconia crown, which provides excellent chewing efficiency, no damage to the opposing natural tooth, having good strength and better esthetics would be the ideal choice.
Zirconia Layered with ceramic are exclusively indicated in replacing anterior teeth where they best mirror adjacent natural teeth.
| Best crown for anterior tooth or implant | Layered zirconia crown |  |
| Best crown for posterior tooth or implant | Monolithic zirconia |  |
| Best bridge for full arch implant | Nexxzr bridge |  |
Difference between Porcelain Fused to Metal, Layered Metal free Zirconia and Monolithic Metal free Zirconia
| PORCELAIN FUSED TO METAL (PFM) | LAYERED ZIRCONIA | MONOLITHIC ZORCONIA |
| Ideal for anterior teeth | Ideal for posterior teeth | |
| Chipping of porcelain is seen over time | Ceramic layering is less likely to chip as the chewing forces are less in the front teeth | No chipping or fracture |
| Abrade opposing natural teeth | Does not affect the opposing natural tooth | Does not affect opposing natural tooth |
| Good strength | High esthetics | High strength |
| Metal Exposure makes it unesthetic | Great esthetics - mimicking natural tooth | Tooth colored |
| Gum tattoo is seen | No gum tattoo | No gum Tattoo |
| More tooth reduction for metal and porcelain layers | Less tooth reduction | Less tooth reduction |
Bridges on teeth
Few cases like a single missing tooth, with inadequate bone to favour implant placement might need a dental bridge i.e., replacing the missing tooth by taking support from adjacent teeth. There are few types of dental bridges which can be used to replace a missing tooth. Certain considerations are however to be made to place a successful bridge.
Types of Dental Bridges:
Traditional Bridges:
Healthy adjacent teeth are used to replace a missing tooth (Pontic).
Cantilever Bridges:

Maryland Bridges:

Implant-Supported Bridges:

Traditional Dental Bridges:

Considerations for Placing a Dental Bridge:
- The healthy natural teeth are to be filed down to take support for missing tooth
- If more teeth are missing, the bridges tend to flex, exerting unequal forces on the supporting teeth.
- The health and longevity of the otherwise healthy teeth are compromised.
- Chances of food accumulation and micro leakage is more when proper marginal fit is not give, leading to caries progression.
- The supporting teeth might need root canal treatment or the periodontal health might be compromised if not properly maintained.
The tooth reduction of supporting teeth might compromise the general health and longevity of the healthy natural teeth.
These bridges tend to flex under constant chewing forces as the missing tooth does not have a proper support of its own. Conditions where more teeth are missing, requiring a long span bridge further flex, exerting unequal forces on the adjacent teeth.
Also, there is a greater chance of food lodgement and caries progression along the margins of the teeth.

All these factors determine the success rate of bridges. Certain modifications in the preparation of teeth, treatment plan and material used to fabricate them will eliminate most of these problems giving a much better prognosis of dental bridges.
Factors Affecting the Prognosis of Crown:
- Amount of tooth/implant reduction
- Flexural Strength of the material
- Fracture resistance of the material
- Marginal fit
- Space between the bridge and the gum
- Span of the bridge
- Health of the adjacent teeth
- Esthetics
How is Metal free Zirconia Superior to Porcelain fused to metal (PFM) in Fabricating Bridges:
Although Porcelain fused to metal (PFM) bridges are widely being used, the newer material Zirconia has many advantages over the former. Few of them are being listed below:

The CAD CAM designed Zirconia metal free crowns offer a precise marginal fit which will give a perfect crown to tooth attachment and does not allow microleakage.
Zirconia being a metal free material is highly biocompatible and does not have any tissue reactions. Hence the missing tooth is made in such a way that there is minimal or no gap between the underlying gum and the tooth. This reduces food lodgement and consequent ill effect on the natural teeth.

Zirconia, have high flexural strength of around 1200MPA and a great fracture resistance. Hence it is indicated in posterior bridges where occlusal forces are more.
CROWNS AND BRIDGES ON IMPLANTS
Having known all the advantages of Metal free Zirconia over Porcelain fused to metal crowns, it is also imperative to know which crown to choose over implants. There are two types of dental implant systems being used.

Single-Piece Basal Implant – The entire implant comprises of a single component with self incorporated abutment.
This implant design determines how the permanent crowns/bridges are fixed onto them. When multi unit implants are used, to place a PFM/Zirconia bridge, a metal sleeve is made in the metal core, which helps in fixing the bridge to implants with the help of a screw.
Apart from all the advantages of zirconia over PFM, which were described, when crowns/bridges are placed over implants, certain additional factors are considered to allow better retention and their prognosis.
Factors Determining the Prognosis of Bridges over Implant:


Using a single piece implant, eliminates this metal sleeve, as the abutment is self-incorporated, and is not fixed with mini screws. It also greatly reduces the additional 
High Strength of monolithic Zirconia (metal free) even at a minimum thickness (as low as 0.5mm) makes it possible to maintain the height of the abutment. Adequate height of these abutments increases the surface area for cement to properly adhere the bridge to implants, ameliorating the long-term retention of bridge.
Full Arch Bridge Over Implants:
Rehabilitation of full mouth with dental implants largely increases the span of the bridge. As said earlier, a long span bridge tends to flex more under forces. This poses a great challenge in proper treatment planning. Few features of concern would be:
- How many implants are to be placed?
- Where should the implants be placed
- Span between two implants
- Type of implant system used (Multi unit or single piece)
- What material is used (PFM or Zirconia)
- Which type of Zirconia (metal free crwons/bridges) is to be used (monolithic or layered)
- What is a NexxZr bridge?
- What are the benefits of using NexxZr Bridge?
Since full mouth rehabilitation requires a very long span bridge, it is very important to place adequate number of implants to give stable support to the overlying bridge. This varies from patient to patient and is determined by the
- Size of the arch
- Quantity and quality of available bone
- Proximity to vital structures.
These factors are analyzed in the 3D scan and implants are placed in places where proper anchorage is gained.
The distance between two consecutive implants is also determined by the fact that it offers adequate stability and support to the bridge.
When multi-unit implants are used, the abutment is screwed separately, the size of this abutment is chosen according to the space available between the two jaws. Single piece implants, with self-incorporating abutment are trimmed to gain adequate space for both the bridges (Upper and lower).
Thus when using Porcelain fused to metal bridges or layered ceramics, more space is needed to accommodate both the upper and lower bridges, greatly compromising the size of the implants (or abutments) and therefore retention of bridges.
Monolithic Zirconia, having a great fracture resistance and flexural strength, makes it an ideal choice for posterior dental bridges. But when anterior teeth are replaced, monolithic Zirconia does not provide adequate esthetics. This led to the invention of many brands, which are targeting to improve the translucency of Zirconia (metal free).
NexxZr Bridge:
NexxZr bridge is a complete zirconia bridge, which is a combination of monolithic metal free Zirconia on the posterior teeth and layered metal free Zirconia on the anterior teeth.
Advantages of NexxZr Bridge:
- Consists of Monolithic Metal free Zirconia crown on the posterior teeth, which are more prone to chewing forces. The high strength makes it the ideal choice to take high chewing forces at a minimum thickness, without compromising its strength.
- The anterior bridge can however be layered with ceramic material, making it highly esthetic.
- As the Zirconia bridge does not require more space between the two jaws, the height of the abutments are only minimally reduced, increasing the retention of bridges.
- The bridges are cemented onto the implants, and not screwed. This eliminates the metal sleeve and doesn’t compromise the mechanical strength.
- CAD CAM designing of the bridge provides precise marginal fit.
- Highly esthetic with great translucency, giving a natural appearance of the bridge.
- Does not chip/fracture
Please take a moment to listen to what patients from around the world have to say about their experience with Dr. Motiwala.
Maria Stubbs (Australia)
Australian woman shares her experience of Smile Makeover in India.
Anita (United Kingdom)
Anita shares her upper full arch implant experience 1 year post treatment.
Doris Shaw (Florida, USA)
Florida woman flies to India for full mouth dental implants.
COST OF METAL FREE ZIRCONIA CROWNS IN INDIA
| NEXXZR ZIRCONIA CROWN TREATMENT (All Prices in USD$) | USA | INDIA | SAVING ($) | SAVINGS (%) |
| Single zirconia crown | $1,600 | $200 | $1,400 | 87.5% |
| Smile-Design with NexxZr Zirconia Crowns | $19,200 | $2,400 | $16,800 | 87.5% |
| Upper front 6 units of Zirconia Crowns / Bridge | $9,600 | $1,200 | ||
| Lower front 6 units of Zirconia Crowns / Bridge | $9,600 | $1,200 | ||
| Full Smile Makeover with NexxZr Zirconia Crowns | $32,000 | $4,000 | $28,000 | 87.5% |
| Upper front 10 units of Zirconia Crowns / Bridge | $16,000 | $2,000 | ||
| Lower front 10 units of Zirconia Crowns / Bridge | $16,000 | $2,000 | ||
| Full Mouth Restoration with NexxZr Zirconia Crowns | $44,800 | $5,600 | $39,200 | 87.5% |
| Upper full arch 14 units of Zirconia Crowns / Bridge | $22,400 | $2,800 | ||
| Lower full arch 14 units of Zirconia Crowns / Bridge | $22,400 | $2,800 |